What is the decomposition time of...?

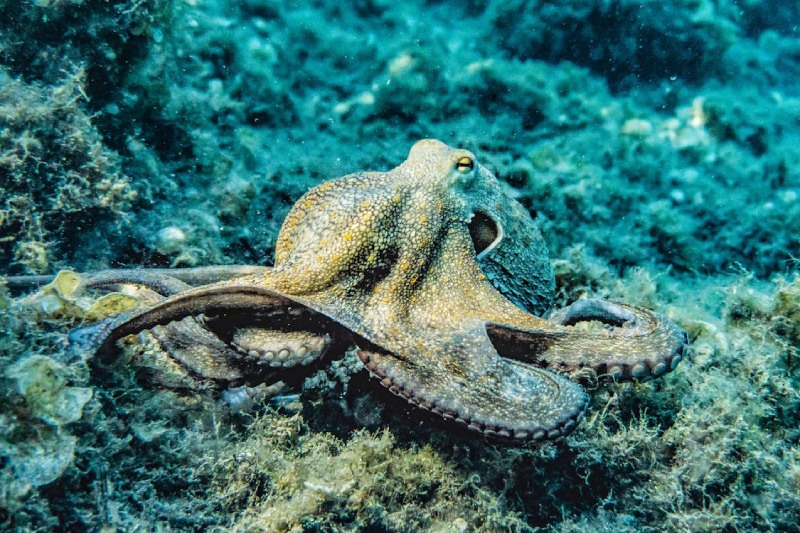
Octopuses, with their eight long arms and bulging eyes, are intelligent and fascinating creatures. But what fuels these enigmatic invertebrates? Let's dive deep and explore the dietary delights of ...
May 13, 2024

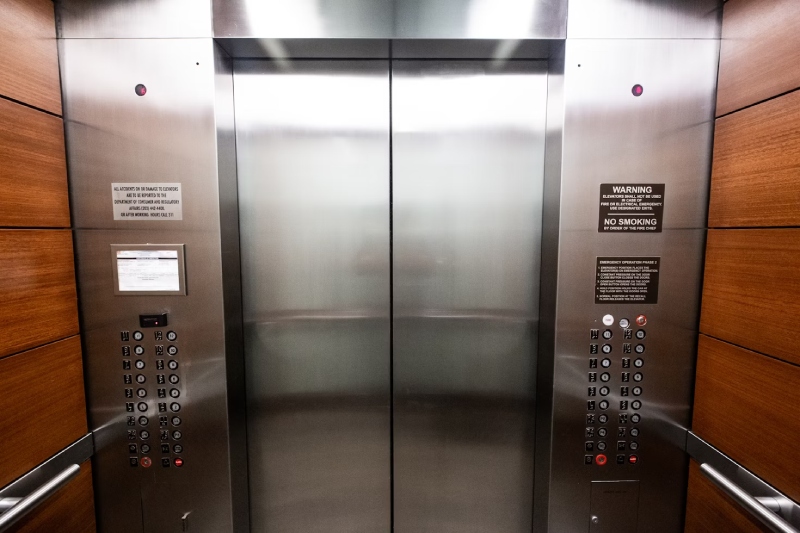
Ever felt lightheaded or unsteady after a quick elevator ride? You're not alone. Many people experience a wave of dizziness after stepping out of an elevator, and it can be quite disorienting. But ...
May 10, 2024

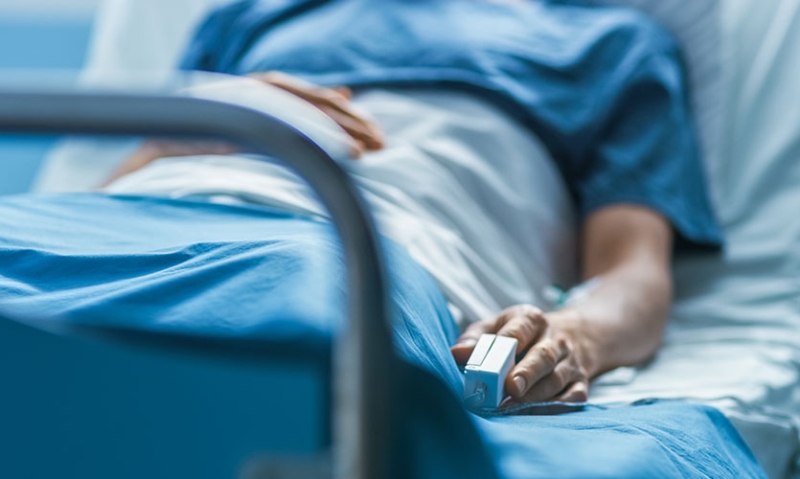
Have you ever bumped your head and felt a sharp sting, only to forget the pain entirely moments later? Or maybe you've wondered if someone in a coma can still experience discomfort. The answer to b...
May 8, 2024

Flamingos, with their vibrant pink feathers and graceful standing posture, are captivating birds found in shallow waters around the world. But what fuels these elegant creatures? While shrimp might...
May 7, 2024

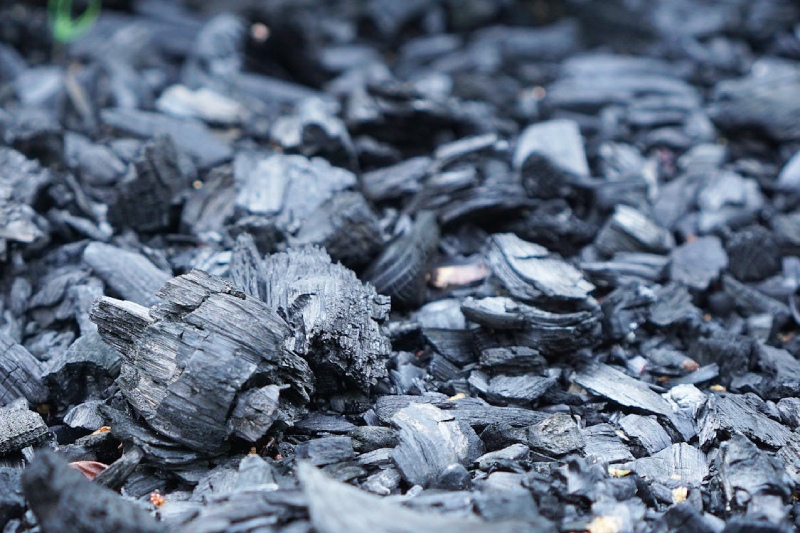
For centuries, charcoal has been used as a natural method for purifying water. But in today's world of complex filtration systems, does charcoal still hold its ground? Let's delve into the science ...
May 7, 2024

We've all been there: that moment of horror when you reach for your toast and discover a charcoal briquette instead of a golden slice. The question arises - is slightly burned toast a dietary disas...
May 3, 2024
For over 170 years, mercury thermometers have been the go-to tool for measuring temperature. But why mercury? This article explores the properties that made it the ideal choice, along with the safe...
May 2, 2024

Copper is a metal commonly found in plumbing pipes, electrical wiring, and even some cookware. But what happens when this reddish metal comes into contact with water? The answer depends on the dura...
April 30, 2024

Lakes, those glistening bodies of water nestled amongst mountains or sprawling across plains, might seem like temporary features. After all, shouldn't all that water eventually seep down into the g...
April 29, 2024

Reality star and television personality Natalie Nunn has garnered attention for her glamorous looks and bold personality. But in a recent turn of events, Nunn has surprised fans by openly embracing...
April 26, 2024
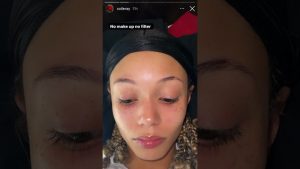
Coi Leray, a rising star in the music industry, has become a beacon of self-love and acceptance through her consistent promotion of the no-makeup look. This article explores Leray's impact on the b...
April 26, 2024

In the ever-evolving world of weight loss trends, a new concoction has bubbled to the surface: coffee with baking soda. But before you brew a pot and grab the baking powder box, let's separate fact...
April 25, 2024

For many, a steaming cup of coffee is the fuel that jumpstarts the day. But achieving that perfect cup isn't just about the beans you choose – it's also about the precise amount of coffee grounds y...
April 25, 2024

Members of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, often referred to as Mormons, are widely known for abstaining from coffee. This practice stems from a tenet called the Word of Wisdom, a ...
April 25, 2024

We've all been there: reaching for a quick cup of coffee only to discover the dreaded "best before" date has passed. But with 3-in-1 coffee packets containing sugar, creamer, and instant coffee, is...
April 24, 2024

For many, the aroma of freshly brewed coffee is the cornerstone of a good morning. But what happens when that bag of grounds lingers in the pantry for months, or even years? Is that 10-year-old cof...
April 24, 2024

Coffee lovers know the importance of a fresh cup. But once those beans are ground, their vibrant flavor starts a slow decline. Let's delve into the science behind ground coffee degradation and how ...
April 24, 2024

For many health-conscious consumers, the lingering presence of pesticides on fruits and vegetables is a concern. Baking soda has emerged as a popular household solution for removing these residues....
April 23, 2024

Ever wondered if that quick rinse under the tap is enough to remove dirt, pesticides, and bacteria from your fruits? Many people turn to natural cleaning solutions like vinegar and baking soda for ...
April 23, 2024

For centuries, people have sought natural ways to achieve healthy, radiant skin. Flaxseed, a tiny but mighty seed, is emerging as a popular choice for promoting a natural glow from within.
Flaxs...
April 23, 2024
✅ 10 most ecologically clean countries in the world 🌎
Switzerland
Sweden
Finland
Norway
Germany
Austria
Iceland
Denmark
New Zealand
Canada
🔝 Popular posts
What types of secondary raw materials do we distinguish?
There are several types of secondary raw materials, including:
🟩 Recycled Metals
These include metals such as aluminum, steel, copper, and lead, which are recovered from scrap and waste materials like old vehicles, appliances, and electronic devices.
🟩 Recycled Plastics
Plastics from used containers, packaging, and other plastic waste can be recycled and converted into raw materials for manufacturing new plastic products.
🟩 Recycled Paper
Paper and cardboard products, like newspapers, magazines, and used cardboard boxes, can be recycled to produce new paper and paper-based products.
🟩 Recycled Glass
Glass bottles and containers can be recycled and processed into raw materials for making new glass products.
🟩 Recycled Textiles
Textiles and clothing can be recycled to create secondary raw materials for making new fabric and clothing items.
🟩 Recovered Energy
Waste-to-energy processes can extract energy from waste materials, such as incineration of non-recyclable waste, to generate electricity or heat.
🟩 Recycled Electronic Waste (E-waste)
Electronic waste, including old computers, smartphones, and other electronic devices, can be processed to extract valuable metals and components for reuse.
🟩 Reclaimed Wood
Wood from demolished buildings or used wooden products can be salvaged and reused as secondary raw materials for construction and other applications.
🟩 Regenerated Fibers
Some fibers, like polyester and nylon, can be chemically processed from post-consumer waste, such as plastic bottles or discarded textiles.
🟩 Recycled Rubber
Rubber from discarded tires and other rubber products can be recycled and used in various applications, including in manufacturing new tires.
These secondary raw materials play a vital role in promoting sustainability and reducing the environmental impact of industrial processes by reducing the need for virgin raw materials and minimizing waste generation.
TOP 5 products commonly made from recycled materials
♻️ Recycled Paper Products
Various paper products, such as notebooks, tissue paper, cardboard boxes, and printing paper, are often made from recycled paper fibers. Recycling paper helps conserve trees and reduces the demand for fresh wood pulp.
♻️ Recycled Plastic Products
Plastic bottles, containers, bags, and other plastic items can be recycled and transformed into new products like recycled plastic bottles, packaging materials, outdoor furniture, and even clothing.
♻️ Recycled Aluminum Products
Recycled aluminum is used to manufacture a wide range of products, including aluminum cans, foils, kitchen utensils, and parts for automobiles and bicycles.
♻️ Recycled Glass Products
Glass bottles and containers can be recycled to create new glass products, such as new bottles, jars, glassware, and even countertops and decorative items.
♻️ Recycled Tire Products
Used rubber tires are recycled and repurposed into various products, such as rubberized playground surfaces, athletic tracks, automotive parts, and even rubberized asphalt for road construction.




